”Critical mass -rare earth elements." 01 January 12, Materials World Magazine -Members only feature- by Prof. Animesh Jha’s is an excellent succinct overview of the wide and complex fields involving Rare Earth Elements,(REE’s) Jha provides pointers and answers to many aspects in his near “cradle to grave” approach.
The issues at hand
“There are constant warnings about the risks of
exhausting supply of vital resources, including the impact on our way of life.
Professor Animesh Jha, from the Institute for Materials Research at the
University of Leeds, UK, examines the sources of rare earth elements and the
research driving their use in emerging technologies.”
Prof. A. Jha provides pointers and answers to the
following 5W’s type questions
on REE:
What they are, why they are
important and to whom, what is global demand now and in the future (when), past
present and future price evolution, based upon recent results and
sustainability consideration in terms of resources and competition for energy,
renewable energy.

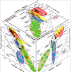
Fig2 RHS. shows the relative abundance in the earths crust (not the ease of economical exploration and mining)
MORE ADVANCED_FUNDAMENTAL STRUCTURES:-
Why they are important and to
whom
-Motivation for Change and Innovation.
Prof. Jha focuses our attention on the essential role
played by REE in a modern sustainable economy, quote: ”The REE supply chain (directly)
affects three main sectors of the world economy – 1.energy, 2. health, and 3.
digital and indirectly via 1 and 2 impacts upon the natural and built
environments, and therefore on long-term climate change.” A powerful motor for
growth is: “the world’s desire for developing cleaner and more energy efficient
magnetic and electronic devices, including: displays, computer hard drives,
wind turbines, fuel cells, hydrogen storage materials, efficient high-power
lasers and amplifiers for materials processing and optical communication
systems...”
“Scientifically (and this is an important factor to
achieving successful results) the 17 REE’s are inspiring due to their rather
unusual combination of properties, manifested by their electronic and nuclear
structures. This explains why they have found a multitude of applications in
technology.” ( as above list)
We can safely
deduce that such materials are promised an impressive long-term future due to
their role in the "indispensables devices of modern life" and the coming “green technology”.
What is (cf. Fig3). Global Supply and Demand, production tonnage, evolution and projection, relative supply share and market share )
“China is the current major player in the supply of these elements.” Indeed this situation has stimulated energetic response from the rest of the world-ROW (JOBS?) in order to avoid or at least attenuate the probable OPEP like position held by China. 

How to alleviate resource availability_Solutions.
Prof. Jha makes a
clear case for finding new sources of REEs and for recycling them due to their
importance in order to achieve a sustainable economy.
His analysis is succinct
but all main issues are introduced, His arguments are based upon market
dependence, technical, geological and mining considerations of these not so
rare but unevenly distributed minerals and last but not least politico-economic
issues.
Western Europe,
with limited rich natural resources the REO (rare earth oxides) supply tends to
focus on recycling, especially from materials at the end of life.
JOBS and Training for R and D,
Minerals Exploration, Mining and Materials, Industries and Commerce.
“Although recycling
REOs is an important area for growing new types of commercial activities, it is
unlikely to meet the rising demands in the energy and digital sectors”. (I
translate this as a source of much needed SUSTAINABLE JOBS.
“If Europe focuses
on research and development for cleaner technology based on REEs, there might
be a joint opportunity to work with major mining companies outside China (95%
of REE mineral sources) for creating healthy competition and industry.”
NB.
I guess there is
an excellent opportunity for Jobs here– I recently learned that an old
university classmate, instead of taking a well earned retirement, decided to
take a position with as Senior Project Manager with a Canadian Rare Earth Exploration
Company member of The Rare Earth Industry and Technology Association, RITA,based in Colarado,USA.
The EU and naturally the UK
situation are focused upon:
-Critical
materials for the energy and transport sectors (wind turbines, hybrid cars,
hydrogen storage, catalytic converters in auto-motives and fuel cell devices,
and solid-state lighting are listed
-Need to create
research and development capabilities and new opportunities for REE business is
strongly recommended by UK’s Chemistry,
Materials, and Environmental Sustainability Knowledge Transfer Networks (KTN-Innovation
Strategy) KTN-Innovation Strategy Board_Free sign to browse and contribute:
EXTRACTIVE AND
PROCESS METALLURGY
Development of
research and development capability in the UK and the rest of western Europe
has already started.
REE Companies (UK)
Companies Processing Industrially
RE Minerals UK
- Less Common
Metals Company in UK is a major rare earth metal producer,
 - Products
- Products
 - Products
- Products
- Processes
Process steps from Ore benefication to application and market through Oxide, Metal, and Alloy (Fig 4. opposite)
Process steps from Ore benefication to application and market through Oxide, Metal, and Alloy (Fig 4. opposite)
- Metalysis Limited exploits the The
Fray-Farthing-Chen (FFC) Cambridge Process which is a new process for the
extraction of metals and alloys from their solid oxides by molten salt
electrolysis. (cathodic dissociation of metal oxides for electrowinning of
metals)
(Fig 5) The process has a high potential. Initial step up to industrial scale-up has been encouraging with much sought after lower cost Titanium for defence and transport applications.
(Fig 5) The process has a high potential. Initial step up to industrial scale-up has been encouraging with much sought after lower cost Titanium for defence and transport applications.
Rhodia in France (member of the Belgian Solvay Group) is a major player in Rare Earth earth production and marketing. ( Rhodia has recently reached agreement(s) with China Rare Metals and Rare Earth Co., (Dec 12, 2011) with China Rare Metals and Rare Earth Co., Ltd. which is the wholly-owned subsidiary of CHINALCO aiming at integrating and developing the rare earth industry in China.
2 Key features of emerging
trends in REE Process Metallurgical research in the UK according to Jha are :
FURTHER STUDY OF RECYCLING (pdf)
2. - The FFC Cambridge Process has led to commercial exploitation by Metalysis Ltd., UK. The highly desirable electrochemical technique is used for further purification of the RE Oxides RE and RE metals mixture into component metals or alloys, including the production of RE magnetic alloys. The range of Metal Oxides and Minerals is not limited to Rare Earths but can be used to process many otherwise difficult to process metals
NB. For the student or professional reader wishing to pursue FFC Cams process work and Electrowinning in general many papers are freely available via internet eg.
NB. EU-France: Recycling Rare Earth Magnets
or again
Prof Jha’s own pioneering work and approach read in rare elements from waste
“Professor Jha said that not
capturing these rare earth by-products will soon no longer be an option.
“Worldwide richer grades of titanium dioxide minerals are disappearing fast
which means we have to process lower grades of titaniferous minerals and
extract the REO as co-product and not waste them.”
Source: resourceintelligence.net
Valuable rare-earth raw materials extracted from industrial
waste stream 15th Dec 09
A related approach
to determine valuable resources from industrial waste is underway at Durham Uni by The Geochemical Reclamation of Industrial Minerals & Elements (GRIME) research group. (reminds me of our mineral
Resources from Waste
A longer article entitled "Not costing the Earth - unconsidered waste materials" in 01 January 12, Materials World Magazine, cf below.
MAIN CONCLUSIONS (Prof. Jha)
It is impossible to
contemplate a future without rare earth elements.
Although
there is a research initiative within the EU that is inviting bids for basic
research and development in extending knowledge, which aims to supersede the
performance of REO- and metal-based devices. If successful, it will be a
disruptive technology with a time-scale of market entry for such technologies
of at least 10 years.
In the meantime the new and emerging REO must progress
within the EU to support industry.
Geological survey and exploration must continue within the EU and with trading partners for developing novel means of mining and mineral beneficiation.
Geological survey and exploration must continue within the EU and with trading partners for developing novel means of mining and mineral beneficiation.
Deep-sea mining, which carries significant risk and
expense. Such exploration carries incalculable environment cost, concerning the
use of energy intensive equipment and disturbance of the sea bed that is likely
to release trapped greenhouse gases.
The only viable option that
remains is to continue exploring terrestrial sites for REEs, recycle, and
develop new scientific understanding employing nano-science for economising the
use of such sought after materials.
(Please consult the original paper for full article)
OTHER REFERENCES:
OTHER REFERENCES:
Excellent
Comprehensive Website and Indepth Professional Bibliographic Resources
The Geologists too are hard at Work
From the RoyalSociety for Chemistry (RSC) entitled Critical Thinking
"Last October, China started building the world's biggest off-shore wind farm in Bohai Bay, a few hours from Beijing. The country is
constructing wind farms on an unprecedented scale - surely good news given its insatiable appetite for coal. But each megawatt of
power a wind turbine generates requires up to one tonne of rare earth permanent magnets"
"Last October, China started building the world's biggest off-shore wind farm in Bohai Bay, a few hours from Beijing. The country is
constructing wind farms on an unprecedented scale - surely good news given its insatiable appetite for coal. But each megawatt of
power a wind turbine generates requires up to one tonne of rare earth permanent magnets"
LISTE OF IOM3 MEMBER ACCESS FEATURE ARTICLES ON RARE EARTH ELEMENTS.