 Just for the record and future reference this rather (fairly?) wide claim to the realisation of a near "Universal" 3D Materials 3D Simulation Mathematical Model" is Published in Nature Letters under the title "Helical crack-front instability in mixed-mode fracture". by A. J. Pons & A. Karma Notes from Nature Abstract:
Just for the record and future reference this rather (fairly?) wide claim to the realisation of a near "Universal" 3D Materials 3D Simulation Mathematical Model" is Published in Nature Letters under the title "Helical crack-front instability in mixed-mode fracture". by A. J. Pons & A. Karma Notes from Nature Abstract:-Universally unstable:
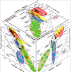
Planar crack propagation under pure tension loading (mode I) is generally stable. However, it becomes universally unstable with the superposition of a shear stress parallel to the crack front (mode III). Under this mixed-mode (I + III) loading configuration, an initially flat parent crack segments into an array of daughter cracks that rotate towards a direction of maximum tensile stress (1).
-Wide Range of Materials:
Wide range of engineering (2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) and geological materials (1, 8).
The link to Nature Abstract are reproduced in references below. Ref 1)
To date at least two Science news sites have echoed the Letter to Nature with descriptions aimed at a more general public.a. ScienceDaily. b. AlphaGalileo
Short extracts from a & b.
a. "Multiscale Materials Model" ScienceDaily
"For the first time ever, a study of this new mathematical model published in Nature has managed to describe the fracture process for materials such as glass, polymers, concrete, ceramics, metals, rocks, and even certain geological fractures."
"Antonio J. Pons, of the research group on Nonlinear Dynamics, Nonlinear Optics and Lasers of the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC)-Barcelona Tech at the Terrassa Campus, has developed a new mathematical model leading to a new law of physics that describes all the stages involved in the way materials crack, making it possible to predict how they will do so before the fracture actually occurs. This is the first time ever that this model has been used to describe objects or materials in 3D, namely all of those that occupy a volume in space and are isotropic, with a homogeneous structure. The study, published in the first week of March in Nature, has been completed in collaboration with researcher Alain Karma, professor at Northeastern University in Boston."(Ref 2)
b. "How some materials break" from AlphaGalileo.
"A material-or, in other words, any solid object or element in our environment-can break in three different ways: from top to bottom (as in the San Andreas Fault, in California); horizontally, like a cut; or as a tear, for instance when a cable is pulled and twisted at the same time.
To set a few other examples, the fault along the Serranía del Interior mountain range in Venezuela cracks following a mixed pattern, combining the first and the third model; the crankshaft in a car motor breaks from torsion and fatigue; an adjustable wrench also breaks from fatigue; polymer materials crack like rocks; objects made of glass break along the same crack lines as geological fractures." Ref 3. below.
Reference
1. 'Helical crack-front instability in mixed-mode fracture', Nature 464, 85-89 (4 March 2010)
Antonio J. Pons(1,2) & Alain Karma(1)
1.Department of Physics and Center for Interdisciplinary Research on Complex Systems, Northeastern University, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA
2.Present address: Department of Physics and Nuclear Engineering, Polytechnic University of Catalonia, Terrassa, Barcelona 08222, Spain.doi:10.1038/nature08862; Received 21 January 2009; Accepted 27 January 2010
ABSTRACT
Planar crack propagation under pure tension loading (mode I) is generally stable. However, it becomes universally unstable with the superposition of a shear stress parallel to the crack front (mode III). Under this mixed-mode (I + III) loading configuration, an initially flat parent crack segments into an array of daughter cracks that rotate towards a direction of maximum tensile stress (1). This segmentation produces stepped fracture surfaces with characteristic ‘lance-shaped’ markings observed in a wide range of engineering (2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) and geological materials (1, 8). The origin of this instability remains poorly understood and a theory with which to predict the surface roughness scale is lacking. Here we perform large-scale simulations of mixed-mode I + III brittle fracture using a continuum phase-field method (9, 10, 11) that describes the complete three-dimensional crack-front evolution. The simulations reveal that planar crack propagation is linearly unstable against helical deformations of the crack front, which evolve nonlinearly into a segmented array of finger-shaped daughter cracks. Furthermore, during their evolution, facets gradually coarsen owing to the growth competition of daughter cracks in striking analogy with the coarsening of finger patterns observed in nonequilibrium growth phenomena(12, 13, 14). We show that the dynamically preferred unstable wavelength is governed by the balance of the destabilizing effect of far-field stresses and the stabilizing effect of cohesive forces on the process zone scale, and we derive a theoretical estimate for this scale using a new propagation law for curved cracks in three dimensions. The rotation angles of coarsened facets are also compared to theoretical predictions and available experimental data.
2. ScienceDaily
3. AlphaGalileo





















No comments:
Post a Comment